DEM20101441
Cornelia Isler-Kerényi
Abstract
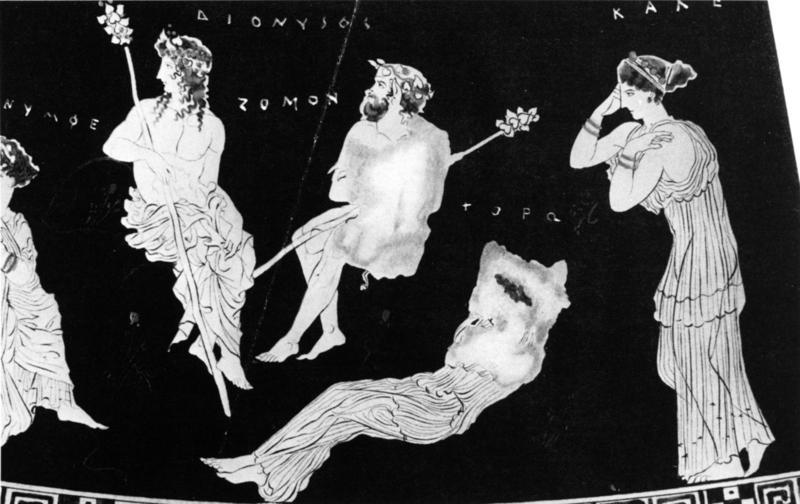
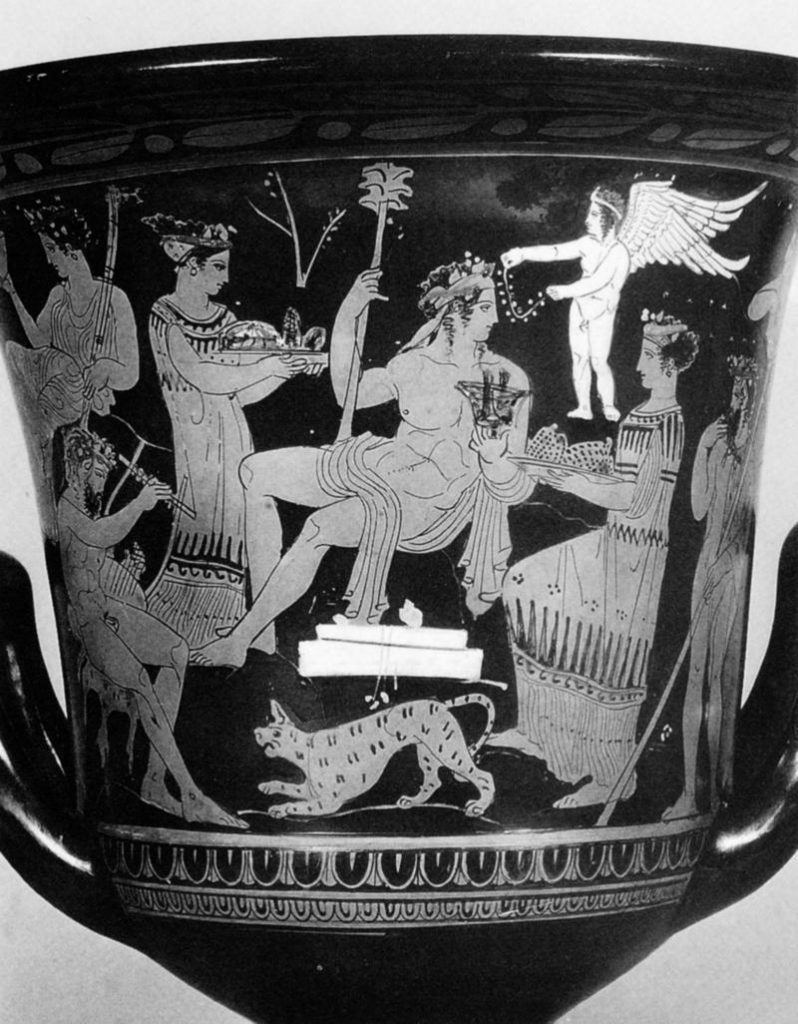
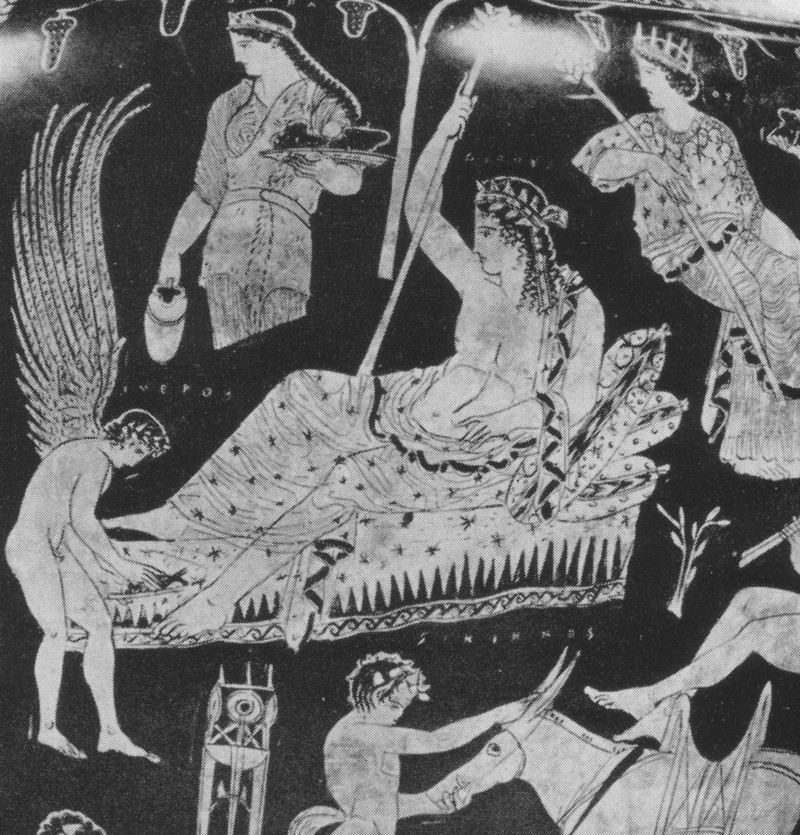
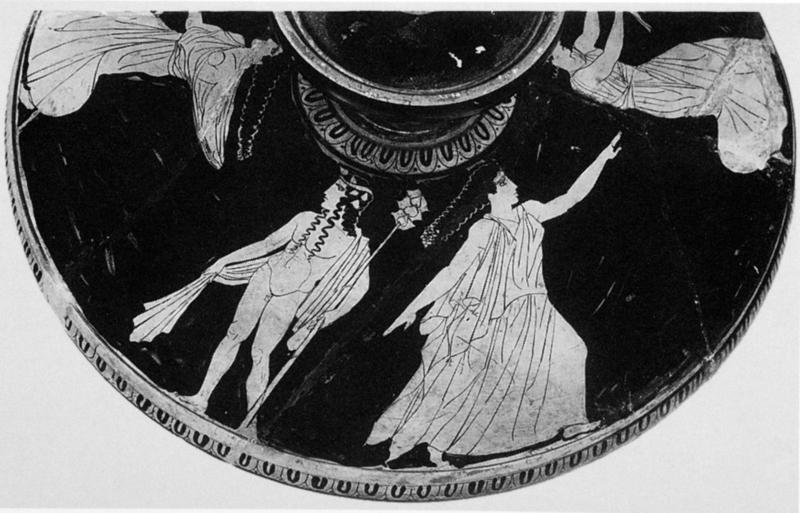
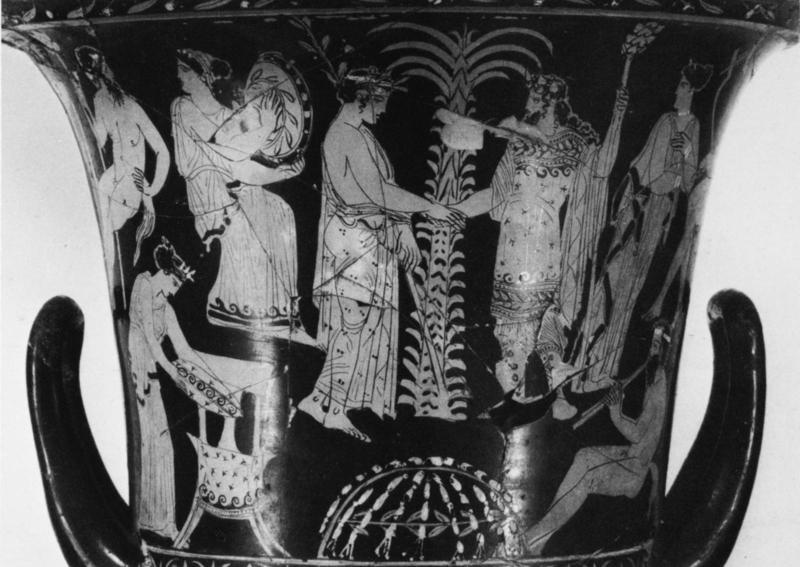
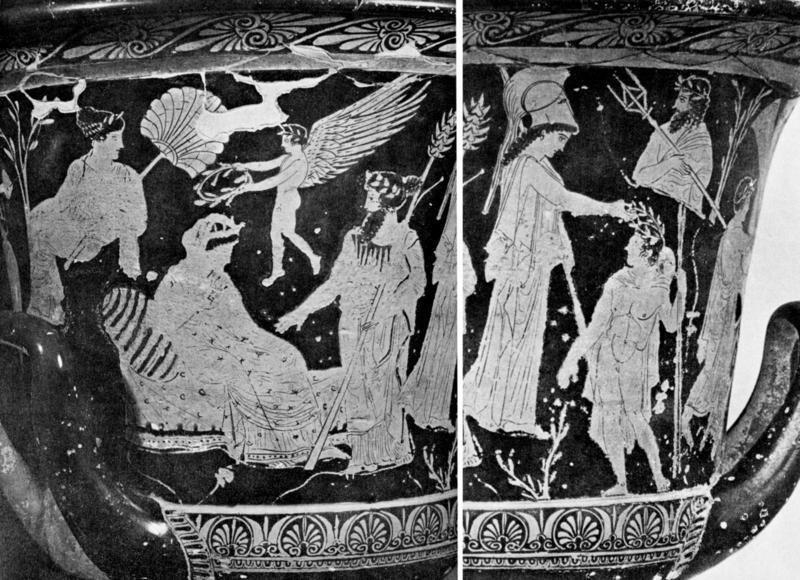
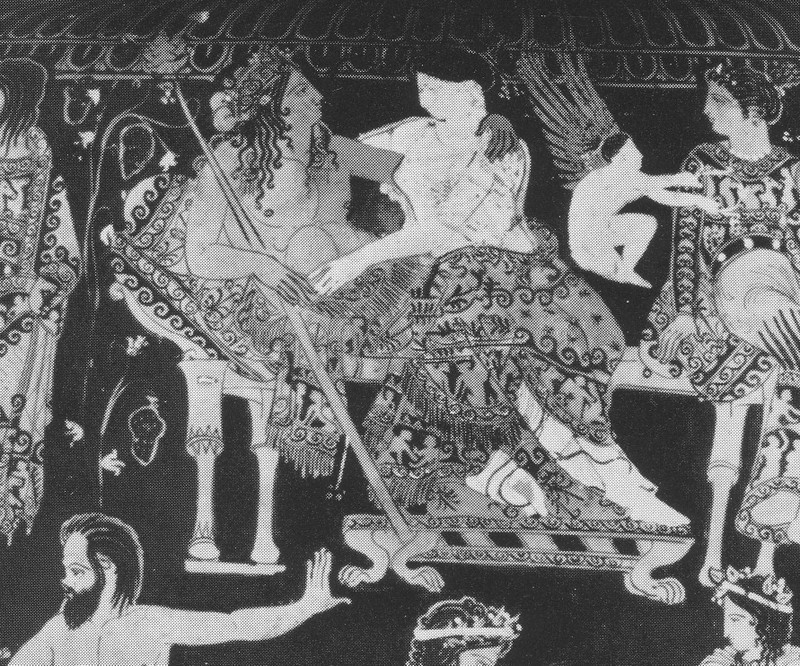
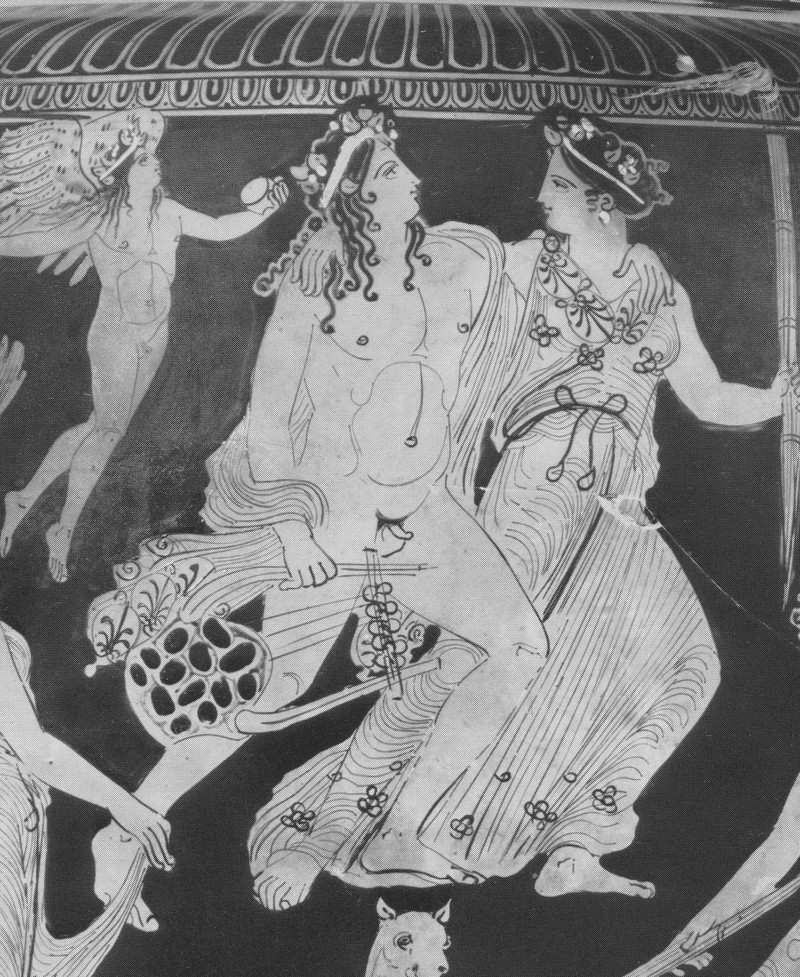
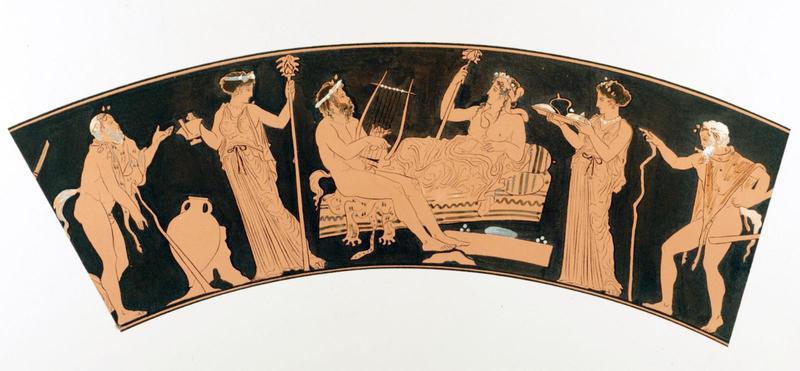
L’inno omerico VII, di datazione controversa, racconta il sequestro di Dioniso nelle sembianze di un efebo da parte di pirati tirreni e il loro castigo. Nella sua iconografia vascolare in età arcaica il dio si presenta invece sempre in età matura. In forme giovanili, come nel frontone est del Partenone, viene raffigurato solo a partire dal 430 a.C. circa. Nel prendere in esame l’immagine di Dioniso nell’opera dei ceramografi ateniesi più importanti attivi in quel periodo si cerca di definire meglio il significato di tale metamorfosi. Essa mette in risalto, rispetto al patrono della polis ufficiale, la divinità dei misteri bacchici rispecchiando con ciò il clima politico e culturale cambiato nell’Atene degli ultimi decenni del V secolo a.C. La situazione iconografica rende difficile immaginare che si potesse cantare il Dioniso efebo prima del 430 a.C.
The Homeric hymn VII, of which the date is controversial, tells of the kidnapping of Dionysus in the guise of an adolescent by a band of Tyrrenian pirates and their punishment. In his ceramic iconography in the Archaic age the God is always represented as a mature man. Only from 430 B.C. is he presented as an adolescent like he is at the East pediment of the Parthenon. Analysing the form of Dionysus in the works of the most important and productive Athenian vase-painters during this period helps us to understand the meaning of such a transformation. These works highlight the divinity of the Bacchic mysteries more than the official patron of the city and reflect the political and cultural climate which changed in Athens in the last decade of the 5th Century B.C. The iconographic situation makes it difficult to imagine that it was possible to sing about an adolescent Dionysus before 430 B.C.
 Scarica l’articolo completo:
Scarica l’articolo completo: